Console
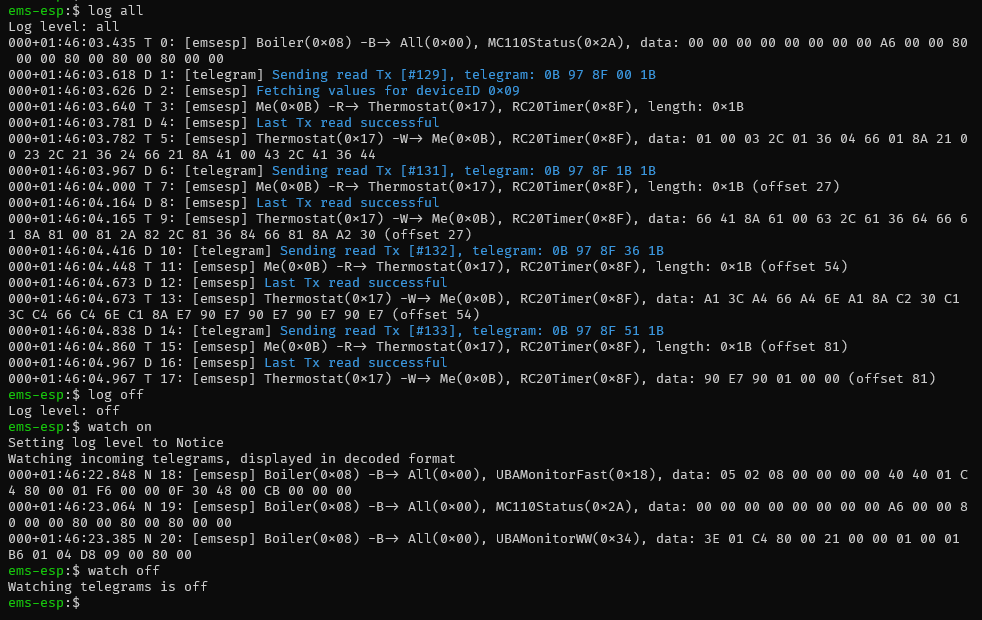
EMS-ESP has a telnet server that enables clients to connect using a telnet client such as PuTTY or natively via the OS like this example with Windows. The port is 23.
You can also access the console via a USB Serial port, using baud 115200. You will need to press CTRL-D to open the Serial console.
The console will give you more insight into the EMS bus traffic, MQTT queues and the full device information its capturing. It behaves similar to a Unix/Linux shell. Some of the most common commands are:
helporF1lists the commands and keywords. This works in each context.exitwill exit the console or exit the current context.CTRL-Ddoes the same.CTRL-Ufor Undo or clearing the line.<TAB>for auto-completesystemto enter the system menu. Useexitor CTRL-D to return.suwill switch to the "super user" or admin mode. The default password isems-esp-neoand can be changed withpasswdfrom the system menu or via the Web interface (called secret password). When in su mode the command prompt switches from$to#.- Some settings can be changed in the console. The
setcommand will list them. showorF2shows the data specific to the which context you're in. From the root it will show you all the EMS device information and any external Dallas temperature sensors.show commandsorcallwill list all the commands which can called with thecallcommand. See Commands.logsets the logging level.log offdisables logging. Uselog debugfor debugging commands and actions,log allincludes the telegrams likewatch on. This will be reset next time the console is opened.watchwill output the incoming Rx telegrams directly to the console. You can also put on a watch on a specific EMS device ID or telegram ID or unknown (new) telegrams. Also choose to output as verbose text as raw data bytes.
Console Commands
Typing help will list the available commands. Some admin commands are only active after first a su command is entered.
exit
help
log [level]
show [system | users | devices | log | ems | values | mqtt | commands
su
passwd
restart [partitionname]
wifi reconnect
set admin password
set wifi password
set hostname <name>
set wifi ssid <name>
set board_profile <name>
set bus_id <deviceID>
set tx_mode <n>
set service <ap | mqtt | ntp> <enable | disable>
scan [deep]
read <deviceID> <type ID> [offset] [length]
watch [off | on | raw | unknown] [ID]
call [device] [cmd] [data] [id|hc]
Examples
Calling a command to change values
Note you have su first to get access to all the call commands.
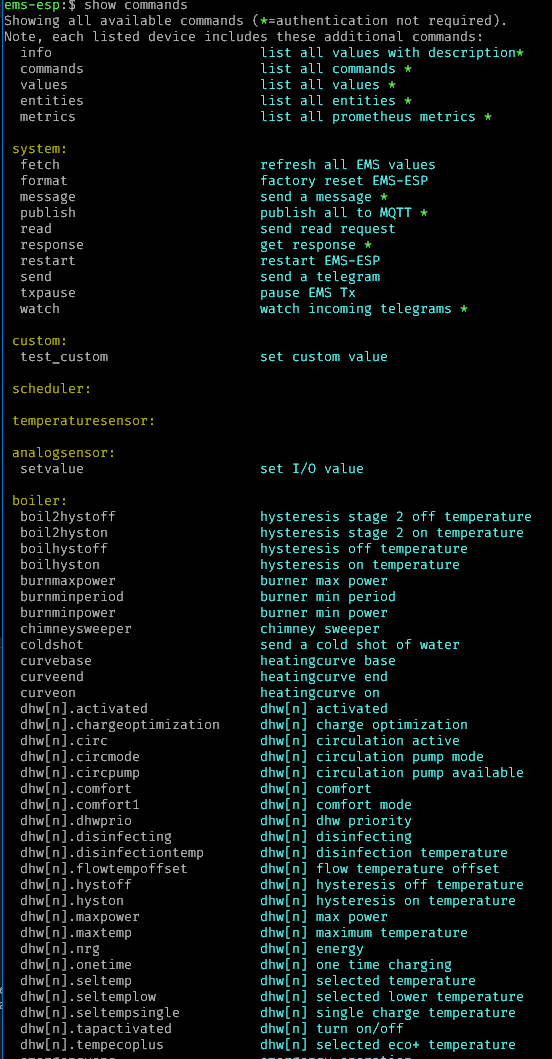
Showing device values
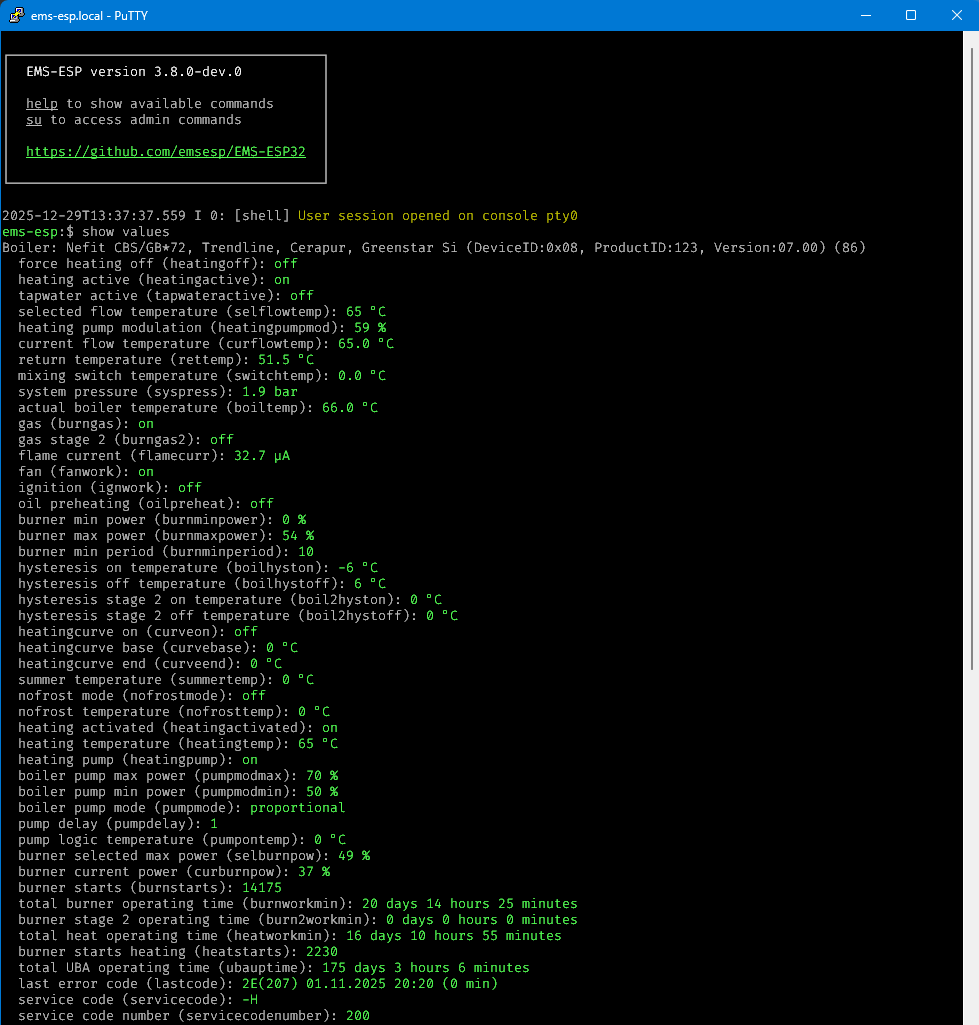
Monitoring the EMS traffic
Using the watch command you can monitor the incoming EMS telegrams.
Syntax is watch on <ID> where ID is either a Telegram ID and also a Device ID.
Note the CRC byte is excluded from the data package.
If you want to see only telegrams that are not registered yet, use watch unknown
If you want to see the raw bytes including CRC as transmitted on the EMS line use watch raw <ID>.